Q1. Can we create a non-web application in Spring Boot?
Yes, we can create a non-web application by removing the web dependencies from the classpath along with changing the way Spring Boot creates the application context.
Q2. Is it possible to change the port of the embedded Tomcat server in Spring Boot?
Yes, it is possible. By using the server.port in the application.properties. server.port=YOUR PORT
Q3. What is the default port of tomcat in spring boot?
The default port of the tomcat server-id is 8080. It can be changed by adding sever.port properties in the application.property file.
server.port=YOUR PORT
Q4. Can we override or replace the Embedded tomcat server in Spring Boot?
Yes, we can replace the Embedded Tomcat server with any server by using the Starter dependency in the pom.xml file.
Q5. Can we disable the default web server in the Spring boot application?
Yes, we can use application.properties to configure the web application type i.e spring.main.web-application-type=none.
Q6. How to disable a specific auto-configuration class?
You can use exclude attribute of @EnableAutoConfiguration if you want auto-configuration not to apply to any specific class.
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={className})
Q7. Explain @RestController annotation in Sprint boot?
It is a combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody, used for creating a restful controller. It converts the response to JSON or XML. It ensures that data returned by each method will be written straight into the response body instead of returning a template.
Q8. What is the difference between @RestController and @Controller in Spring Boot?
@Controller Map of the model object to view or template and make it human-readable.
@RestController simply returns the object and object data is directly written in HTTP response as JSON or XML.
Q9. What is the difference between RequestMapping and GetMapping
RequestMapping can be used with GET, POST, PUT, and many other request methods using the method attribute on the annotation. Whereas getMapping is only an extension of RequestMapping which helps you to improve on clarity on requests.
Q10. What is Spring Actuator? What are its advantages?
An actuator is an additional feature of Spring that helps you to monitor and manage your application when you push it to production. These actuators include auditing, health, CPU usage, HTTP hits, and metric gathering, and many more that are automatically applied to your application.
Q11. How to enable Actuator in the Spring boot application?
To enable the spring actuator feature, we need to add the dependency of “spring-boot-starter-actuator” in pom.xml.
<dependency><groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId> spring-boot-starter-actuator </artifactId></dependency>
Q12. What are the actuator-provided endpoints used for monitoring the Spring boot application?
Actuators provide below pre-defined endpoints to monitor our application -
Health
Info
Beans
Mappings
Configprops
Httptrace
Heapdump
Threaddump
Shutdown
Q13. What is a Swagger in Spring Boot?
Swagger is used for clearly detailing and documenting RESTful APIs in a machine-readable and human-readable format, which is easily comprehensible for testers and developers, as well as individuals having little knowledge of source code.
Q14. What are Profiles in Spring Boot?
Profiles in the Spring framework enable users to map components and beans to specific profiles, such as the Development (dev) profile, Production (prod) profile, or the Test profile. In Spring Boot, the annotation @Profile is used to map components and beans to a certain profile. Developers can also set up profiles using the SpringApplication, for instance, SpringApplication.setAdditionalProfiles("dev"). In another way, While developing the application we deal with multiple environments such as dev, QA, and Prod, and each environment requires a different configuration. To make this easy and clean, Spring has the provision Profiles to keep the separate configuration of environments.
Q15. How to enable debugging log in the spring boot application?
Debugging logs can be enabled in three ways -
We can start the application with the --debug switch.
We can set the logging.level.root=debug property in application.property file.
We can set the logging level of the root logger to debug in the supplied logging configuration file.
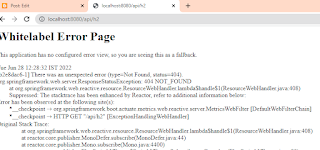
Q16. How to resolve the Whitelabel error page in the spring boot application?
This is quite a common error in the spring boot application which says 404 (page not found).
We can mostly resolve this in 3 ways:
Custom Error Controller– where you will be implementing the ErrorController interface which is provided by SpringFramework and then overriding its getErrorPath() so that you can return a custom path whenever such type of error has occurred.
By Displaying Custom error page– All you have to do is create an error.html page and place it into the src/main/resources/templates path. The BasicErrorController of spring boot will automatically pick this file by default.
By disabling the Whitelabel error page– is the easiest way where all you need to do is server.error.whitelabel.enabled property to false in the application.properties file to disable the whitelabel error page.
Q17. What annotations are used to create an Interceptor?
A prominent functionality of Spring Boot, Interceptor uses the annotated class @Component, and it implements the interface HandlerInterceptor.
The interface contains 3 main methods, which are:
The preHandle() Method − preHandle() is used for intercepting the request prior to the implementation of the handler. If preHandle() returns a “true” boolean value, developers can continue with handler execution. If preHandle() returns a “false” boolean value, developers should stop the handler execution.
preHandle() implementation looks like:
@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o) throws Exception {logger.info(" Pre handle ");if(httpServletRequest.getMethod().equals("GET"))return true;elsereturn false;}
The postHandle() Method − postHandle() is used for intercepting a request following the implementation of the handler. It allows the manipulation of the ModelAndView Object before users render it.
@Overridepublic void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {logger.info(" Post handle ");if(modelAndView.getModelMap().containsKey("status")){String status = (String) modelAndView.getModelMap().get("status");if(status.equals("SUCCESS!")){status = "Authentication " + status;modelAndView.getModelMap().put("status",status);}}}
The afterCompletion() Method − A HandlerInterceptor callback approach, the afterCompletion() method is used when the entire request gets completed.
afterCompletion() looks like:
@Overridepublic void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {logger.info(" After Completion ");}}
Q18. What differentiates Spring Data JPA and Hibernate?
A Java Persistence API (JPA) implementation, Hibernate facilitates Object-Relational Mapping (ORM), allowing users to store, retrieve, map, and update application data to and from Java objects and relational databases. Hibernate maps the data types in Java to SQL (Structured Query Language) data types, and the classes in java to the database tables, relieving developers from scripting data persistence SQL programs.
A Spring Data sub-project, Spring Data JPA, on the other hand, gives abstraction over the DAL (Data Access Layer) by applying JPA and Object–Relational Mapping implementations, such as Hibernate. Spring Data JPA facilitates the smooth implementation of JPA repositories, and it intends to improve the overall implementation of DAL to a great extent.
Q19. How are the @RestController and @Controller Annotations different?
The traditional Spring @Controller annotation specifies that an annotated class represents a controller. It’s basically a @Component specialization, and it is autodetected via the classpath scanning.
The @Controller annotation is used along with the annotated handler methodologies based on @RequestMapping annotations.
Developers use the @RestController annotation to develop RESTful web services, utilizing the Spring Model–View–Controller (MVC).
The Spring @RestController maps the request data to specified request handler methods. Once the handler method generates the response body, the @RestController modifies it to XML or JSON response.
Q20. What are the basic Annotations that spring boot offers?
Core Spring Framework Annotation:-
@Required:- @Required applies to the bean setter method. This indicates that the annotated bean must be populated at the configuration time with the required property; if the following case is not satisfied, it throws an exception BeanInitializationException.
@Autowired:-
In the spring framework, spring provides annotation-based auto–wiring by providing @Autowired annotation. It is used to auto-wire spring bean on setter methods, instance variables, and constructors., When we use the annotation @Autowired, the spring container auto-wires the bean factory by matching the data type.
Other Annotations which are provided by Spring Boot, Spring Framework, and In Spring MVC are:-
@configuartion.
@Componentscan
@Bean
@component.
@Controller
@service.
@Repository
@EnableAutoConfiguaration
@SpringBootApplication.
@RequestMapping
@GetMapping
@PostMapping.
Exception Handling Interview Questions
DBMS Interview Questions Set -1
DBMS Interview Questions Set -2
JPA Interview Questions Set -1
Spring Boot Interview Questions Set 1
Spring Boot Interview Questions Set 2
Core Java Interview Questions Set -1
Docker interview question Set -1
Docker interview question Set -2